Mouth Cancer is not very common, but this is something we do check for at every examination. Even between examinations if your clinician sees you for treatment they will always note if there are any changes to the tissues inside your mouth. Peter has worked in hospital and dealt with various stages of oral cancer in this setting. He is familiar with what to look for and has trained other members of our team to do the same.
FAQ’s
Why Oral Cancer Screening is Important?
We cannot see clearly in our own mouths and so to be assured that a professional is looking at the tissues in your mouth regularly can be reassuring. Regular checks mean that if any signs are spotted they can be investigated and treated at the earliest stage. If you have any concerns about any lesions in your mouth please come and chat to us.
What are the mouth cancer symptoms?
The signs and symptoms of mouth cancer may include, but are not limited to:
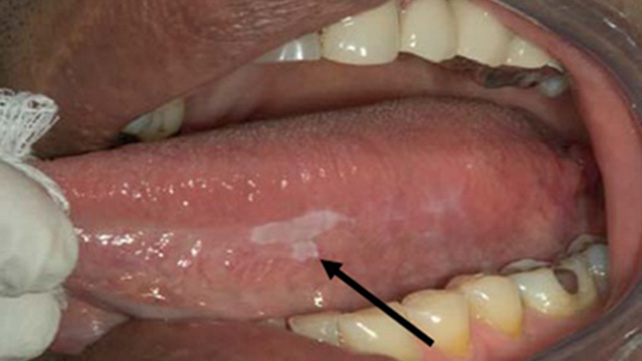
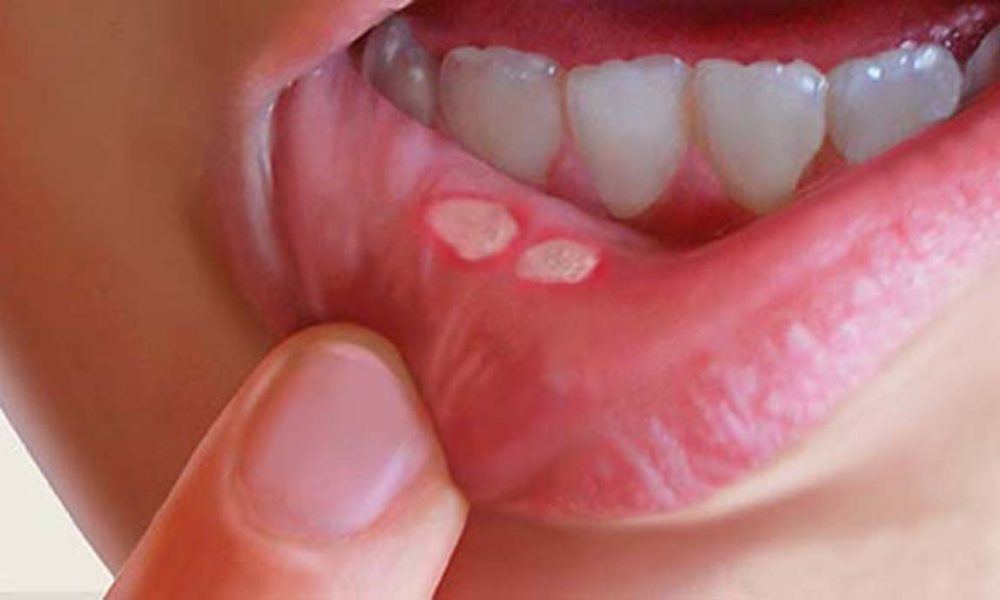
- Persistent mouth sore or ulcer which does not heal.
- A lump or thickening of the cheek.
- Lumps which do not disappear on the floor of the mouth.
- Red or white patches, known as lesions in your mouth or lips.
- Swelling in the mouth which does not go down.
- Persistent numbness, pain or tenderness in and around your mouth, this can include your tongue, lips and cheeks.
- Loose or wobbly teeth with no sign of dental disease.
- Difficulty in moving the jaw or tongue or problems with swallowing and/or speaking
How common is it to get mouth cancer
Mouth cancer accounts for approximately 2% of all cancers in the UK. This amounts to approximately 6800 people per year being diagnosed. Early detection of mouth cancer is of vital importance to increase survival and treatment rates.
What does mouth cancer look like
In his early stages mouth cancer very often causes no pain. The first visible signs are usually white or red lesion or an ulcer, often with a slight depression in the middle. This lesion may often have a grey, yellow or white centre and be red around the edges.
Who is at most risk from mouth cancer
Mouth cancer risk factors depend upon a wide variety of variables including your lifestyle, genetics and other general factors. General oral cancer risk factors include:
- Your gender. Mouth cancer is twice as common in men as it is in women.
- Your age. The average age of diagnosis of mouth cancer is 62 with 66% of all diagnoses happening over the age of 55.
- Smoking. Approximately 80% of all people with some form of oral cancer use tobacco in some form. This can include chewing tobacco or snuff.
- How much alcohol you drink. Of all the people diagnosed with mouth cancer, 70% of them are classified as heavy drinkers. Drinking excessive alcohol clearly increases your risk of mouth cancer.
- HPV virus. The human papilloma virus infection is responsible for one of the biggest increases in mouth cancer. This virus is most commonly spread to the mouth via oral sex.
Is mouth cancer curable
Yes. Mouth cancer has one of the highest rates of successful treatment. However, early detection is vital in order to ensure the rate of recovery remains high. Typically, if oral cancer is discovered early enough survival rates are 90%. Survival rates can drop to 60% after five years of treatment if the cancer has spread prior to diagnosis.
Survival rates for mouth cancer are:
- 84% for cancer that has not spread beyond where it first started
- 64% for cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- 39% for cancer that has spread to distant parts of the body
These survival rates depend upon a range of variables such as:
- Your age.
- Your overall health.
- The stage of cancer when it is initially discovered.
- Your treatment decisions.
- Where the mouth cancer is.
- How the cancer responds to treatment.
How do they test for oral cancer
Diagnosis for oral cancer comes in various stages.
- Initial discovery. Dentists are trained to spot the very early warning signs of oral cancer, your dentist will be able to see things in your mouth which you can’t meaning your dentist is the one most likely to pick up the early warning signs of oral cancer, assuming you visit regularly. If your dentist spots the early warning signs they will refer you to a relevant professional.
- Endoscopy. This allows a doctor to see see deeper into your mouth and throat for a more accurate and close-up visual diagnosis.
- Biopsies. A biopsy can then be taken for examination of the tissue under a microscope.
- Additional diagnosis made him be done using CT or MRI scans.






